Recently, the coronavirus is raging, and people have snapped up various disinfection and antibacterial products. Before becoming one of them, have you ever thought about what you really need or what effect you want to get from the product?
Before that, you need to clearly distinguish the difference between viruses, bacteria and germs. It can help you know what you need and how to choose the product that best suits your needs, so as not to cause unnecessary waste.
Viruses
It is an organic species between living and non-living, living on parasites. It is neither life nor non-life. It currently does not belong to the Five Realms (prokaryotes, protozoa, fungi, plants and animals). Simply put, when the virus finds a suitable host, it will enter some cells in the host's body, allowing the host cell to produce nutrients for the virus to multiply, and finally the host cell will be destroyed, which will lead to developmental diseases of the body. The way to prevent and treat the virus is to vaccinate and take antiviral drugs.
Bacteria
It is a tiny single-celled organic organism that has a great influence on human activities. On the one hand, bacteria are the pathogens of many diseases, including tuberculosis, gonorrhea, syphilis, plague and other diseases are caused by bacteria. However, humans often use beneficial bacteria to make cheese and yogurt and wine, some antibiotics, and wastewater treatment, all of which are related to bacteria. To deal with bad bacteria, antibiotics are generally used to deal with it, so that these bad bacteria can be eliminated or the reproduction speed of bad bacteria can be delayed, so that the immune system can eliminate them.
Germs
In a broad sense, it refers to the microorganisms that make people sick, and the above-mentioned viruses and bacteria are also one of the germs.
Now, after such a simple explanation, do you have a preliminary concept?
The antiseptic alcohol hand rub or wet wipes snapped up on the market will cause protein denaturation after disinfection, leading to the death of bacteria or viruses. However, for some non-enveloped viruses, such as hand, foot and mouth disease (enterovirus E71), rotavirus, and coronavirus infections, alcohol can only inactivate it, but cannot kill it. Please remember that the alcohol concentration directly affects the above effects, not the higher the concentration, the better the effect.
You may ask, is there any other method that can be simpler, more direct, and even more effective?
The answer is yes, that is the ultraviolet rays that we are often exposed to. Ultraviolet disinfection technology can use the appropriate wavelength of ultraviolet rays to destroy the molecular structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) in microbial cells, causing the death of growing cells and/or the death of regenerative cells to achieve a bactericidal effect.
The only minor flaw is that products that use UV disinfection technology are more difficult to find, but rest assured, now I recommend a product that I like very much to everyone, let us fight the epidemic together!
Lexuma XGerm and XGerm PRO multifunctional portable ultraviolet sterilizers use ultraviolet sterilization technology to kill bacteria on most electronic devices, and are easy to use. Electronic novices can easily get started! I think the price is very reasonable and the price-performance ratio is first-rate. I recommend everyone to try it!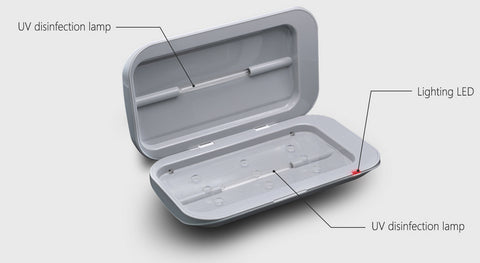
In addition, I would like to give you a small suggestion. After thoroughly disinfecting and sterilizing items, use antibacterial products to reduce the chance of bacteria and viruses reproducing.
The following is another recommendation for my recent favorite-IMC Water Catalyst Continuous Antibacterial Liquid
IMC water catalyst can effectively cover the material to form a grid-like conductive film, which fully penetrates and adheres to the surface of the object. The conductive film generates free radicals to absorb the positrons on the bacteria, making them shrink and difficult to grow. The surface of the material has continuous antibacterial and antiviral effects.






